One of the best writing strategies is to write a lot of bad stuff. Yes, the more bad stuff we write, the better. If that sounds counterintuitive, it is. Here’s how it works.
One reason Beethoven and Picasso produced so many great works was that they produced a lot of ordinary, unknown works. We might know a couple of Beethoven’s nine symphonies, the last of his five piano concertos, his one violin concerto, maybe his opera Fidelio, and probably “Für Elise.” But in his 45-year career, he wrote at least 722 pieces.
He produced twenty variations for piano, dozens of sonatas for piano, for violin, and for cello, chamber music including sixteen string quartets, and more. Yet only a few are in the standard canon of often-played pieces; only a few are considered masterpieces.
We know Picasso as the twentieth-century artistic genius who created Guernica, the sculpture in Chicago’s Daley Plaza, and stunning abstract portraits. But he produced “more than 1,800 painting, 1,200 sculptures, 2,800 ceramics, 12,000 drawings as well as prints, rugs and tapestries—only a fraction of which ever garnered acclaim.”*
We know creative geniuses for their few great works. What we don’t know is that in general they simply outproduced their peers. Creating so much increased their odds that a few would be landmark creations.
We shouldn’t be afraid to create junk or to write something that’s ordinary. For thirteen years I have been blogging at Andy Unedited. In that time I have produced over six hundred posts. I do my best but most of them are just OK. A few, I think, are very good. Yet I wouldn’t have written any good ones if I didn’t have the discipline of trying to produce something every week, including the commonplace ones.
A second upside down writing strategy is to do stuff besides write. Studies have shown that scientists are twelve times more likely to win a Nobel prize if they write poetry, plays, novels or other works, than if they don’t. And twenty-two times more likely if they perform as an amateur actor, dancer, or magician.** To be more creative with our writing we should branch out.
If you write mystery novels, experiment with poetry. If history is your field, try literary fiction. Take up a musical instrument, go to museums, do some painting, throw clay pots, immerse yourself in Japanese culture. As I say in chapter 11 of Write Better, when we have a wider range of new experiences and ideas that we are exposed to, the more we will make interesting connections that can inspire our writing.
A third strategy: Don’t start at the beginning. If you are writing a book, don’t start with the first chapter, start with the easiest chapter—the one you’ve thought about a lot already.
If you are writing a chapter or an article, don’t begin with the first paragraph. Start with the easiest thing for you to write, whatever comes to your mind. It doesn’t have to be great or even good. It just has to be there. You can (and should) always revise later.
I emphasize this strategy with writers because it is the one piece of writing advice that I give to myself most often. Every time I sit down to write, I pause. and tell myself, don’t worry about where to start. Just start . . . anywhere, with any related or semi-related idea or story, whether good or bad. Just start.
What writing strategies have you found helpful?
—
*Adam Grant, Originals, p. 36.
**Adam Grant, Originals, p. 47.
Credits: Daley Plaza (www.chicago.gov); Guernica (Pixabay, Almudena Sanz Tabernero)
 Unfortunately, the “singular they” has become so common that it is often used when it is just not necessary. Consider:
Unfortunately, the “singular they” has become so common that it is often used when it is just not necessary. Consider:
 Bryan Stevenson’s
Bryan Stevenson’s 
 Buy-In. David Logan, professor at the University of Southern California’s Marshall School of Business notes: “Asking for someone’s ‘buy-in’ says, ‘I have an idea. I didn’t involve you because I didn’t value you enough to discuss it with you. I want you to embrace it as if you were in on it from the beginning, because that would make me feel really good.’”
Buy-In. David Logan, professor at the University of Southern California’s Marshall School of Business notes: “Asking for someone’s ‘buy-in’ says, ‘I have an idea. I didn’t involve you because I didn’t value you enough to discuss it with you. I want you to embrace it as if you were in on it from the beginning, because that would make me feel really good.’”


 Caro’s other passion is explaining how political power works because it has a tremendous effect on our lives. Robert Moses was determined to reshape New York City with bridges, highways, parks, and other public works. To do so, during his forty years in power, Moses displaced a half million of New York’s fourteen million people—forcing them out of their homes, destroying communities. In a democracy, Caro wants us to know how that kind of power (of an unelected official) works.
Caro’s other passion is explaining how political power works because it has a tremendous effect on our lives. Robert Moses was determined to reshape New York City with bridges, highways, parks, and other public works. To do so, during his forty years in power, Moses displaced a half million of New York’s fourteen million people—forcing them out of their homes, destroying communities. In a democracy, Caro wants us to know how that kind of power (of an unelected official) works.
 Advice That’s Out of This World
Advice That’s Out of This World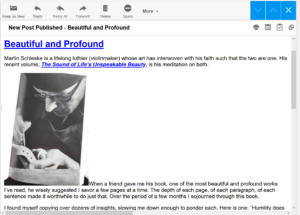 Some of you who subscribe to Andy Unedited have mentioned that the font size is small in the email alert you receive. If you just click on the headline of the blog found in the email, you will be sent to the blog website which is much more readable. (So, for example, if you get this in an email, put your cursor on “Tuesday Round Up” in the email and then click! Easy as eating pumpkin pie.)
Some of you who subscribe to Andy Unedited have mentioned that the font size is small in the email alert you receive. If you just click on the headline of the blog found in the email, you will be sent to the blog website which is much more readable. (So, for example, if you get this in an email, put your cursor on “Tuesday Round Up” in the email and then click! Easy as eating pumpkin pie.) My wife and I recently rented the DVD of this gripping story of two British soldiers in World War I who make an amazing 24-hour journey to deliver a message that could save hundreds of lives. The unusual use of only one camera during the entire film heightens not only the immersive immediacy of the movie but the dogged courage of this pair.
My wife and I recently rented the DVD of this gripping story of two British soldiers in World War I who make an amazing 24-hour journey to deliver a message that could save hundreds of lives. The unusual use of only one camera during the entire film heightens not only the immersive immediacy of the movie but the dogged courage of this pair.
 And what is the difference between giftables and gifts? Two extraneous syllables and four unnecessary letters! What could possibly justify creating a gratuitous adjective just to make it into a noun? And don’t get me started on using too many exclamation points!
And what is the difference between giftables and gifts? Two extraneous syllables and four unnecessary letters! What could possibly justify creating a gratuitous adjective just to make it into a noun? And don’t get me started on using too many exclamation points!
